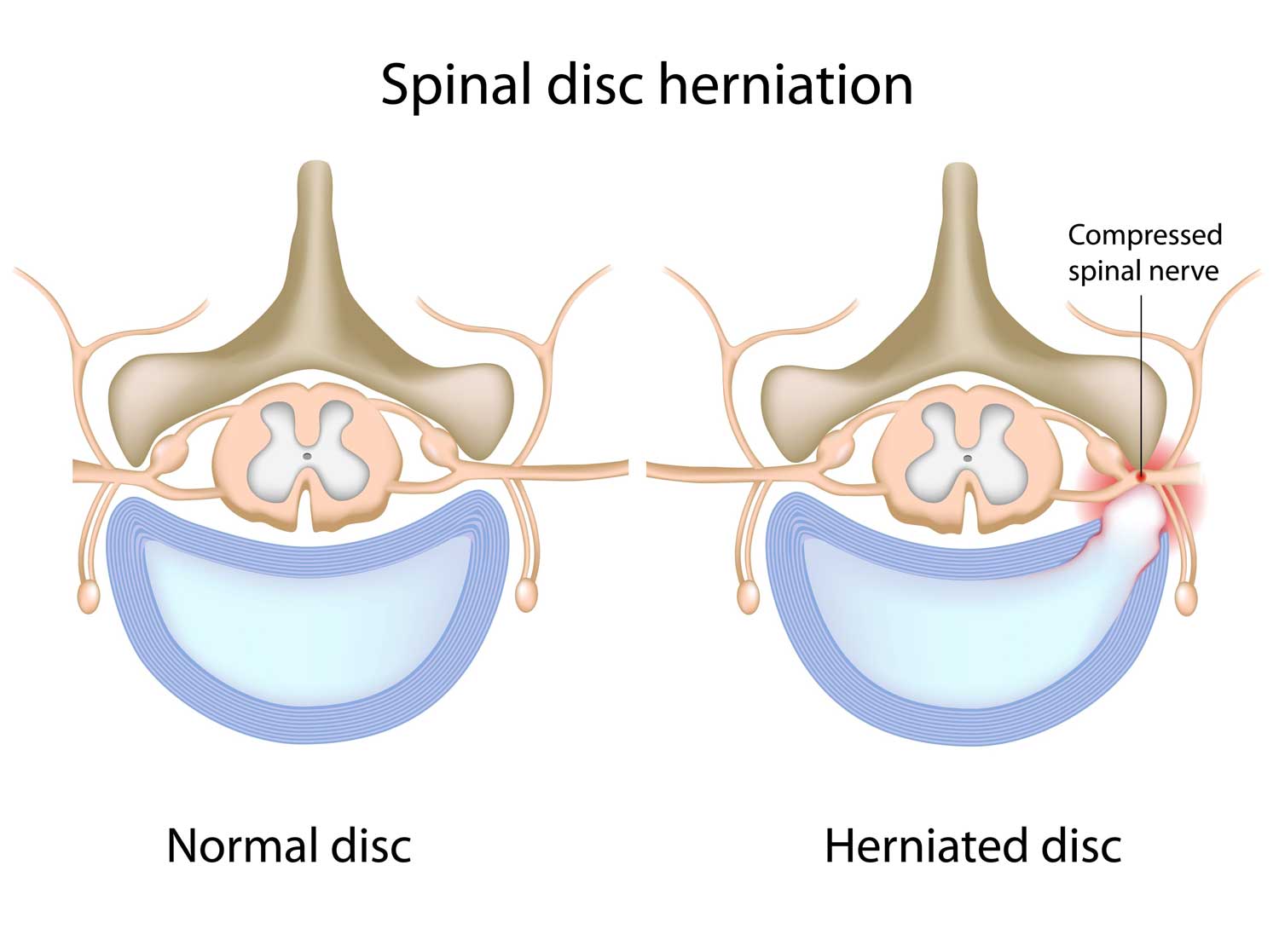
Risk Factors for a Herniated Disc
A herniated disc can occur at any age, but it usually happens to people who are in their 20s or 30s. Here are some risk factors:
- Genetics - The predisposition to herniated disc might be inherited
- Lifestyle - Lack of regular exercise, smoking, and nutrition deficiency can be a significant influence to poor disc health
- Occupation - Physically demanding jobs that require bending, lifting, pushing, pulling and twisting can increase the likelihood of herniated disc
- Posture - Poor posture can strain the spinal discs in the lower back
- Weight - Excessive body weight puts more pressure on the discs in the lumbar spine - this may lead to herniated discs or spinal osteoarthritis, resulting in lumbar stenosis
Herniated Disc Diagnosis
In most cases, the doctor can diagnose a slipped disc through a physical or neurological exam and a review of the patient's medical history. However, if the doctor needs more information about the disc problem, one or more of the following tests might be requested:
Nerve tests
These tests help find the location of the nerve damage as they evaluate how well the electric impulses move along with the nerve tissue. It also measures the electrical activity of the muscles when they're active and stationary.
Imaging tests
- X-rays
Ordinary x-rays are performed not to detect slipped discs, but to exclude the other possible causes of back pain.
- Computerized tomography (CT scan)
A CT scan is performed to determine the location and degree of the disc impairment. It shoots a series of x-rays from various directions and combines them to generate the cross-sectional images of the spinal column and the parts around it.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
MRI is used to identify the specific position of the slipped disc and affected nerves. It helps to delineate the severity of the spinal condition. This imaging test utilises strong magnetic pulses in order to generate detailed images of the body's internal structure. Contrary to popular belief, there is no radiation involved in MRI scans.
- Myelogram
This CT-assisted imaging test can display the pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, as a result of herniated discs and other conditions. Some patients who are not suitable for MRI may opt for this procedure instead.
Surgical Treatment for Herniated Disc
For mild to moderate pain, over-the-counter pain relievers may suffice. If the pain does not subside, or is coupled with muscle spasms, the doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants, nerve stabilizers and narcotics, which will be taken for only a short time and under close supervision.
Severe pain from nerve compression may also be alleviated using cortisone and epidural steroid injections.
Additionally, physiotherapy and lifestyle changes are advised to help the patient manage and reduce the pain caused by a herniated disc.
However, if symptoms persist, then surgical treatment may be recommended:
- Microdiscectomy
Usually recommended if the cause of sciatica pain is due to a herniated disk. Generally patients who don't recovery after some non-operative treatment may opt for surgery. A microscope is usually used to perform microdiscectomy, and the incision is usually minimal.
- Lumbar Laminotomy or Laminectomy
These procedures can alleviate nerve compression, sciatica, and leg pain. Both treatments involve the removal of part or all of the vertebral lamina, a bony structure that forms a protective covering for the spinal nerve roots to better access the slipped disc.
- Nucleoplasty
For selected cases, some patients may be suitable for this truly minimally invasive procedure, using a small pin-point radiofrequency probe. This sometimes is performed as a day surgery case. The patient does not need to stay overnight in the hospital. However the doctor will need to assess the patient's suitability.
- Spinal Fusion
This procedure aims to stabilize the spine and at the same time decompress the spinal nerves thru a combination of the surgical methods of spinal decompression described above. It may require screws to complete the construct, and aid the patient recover faster thru immediate stability.
- Artificial Disc Surgery
Artificial disc surgery, or total disc replacement, involves removing the worn or damaged disc and replacing it with an artificial plastic, ceramic or metal implant. Doing so can help alleviate pain, and at the same time maintain smooth movement in the spine.
Herniated Disc Prevention
A herniated disc is often caused by spinal overuse, trauma or gradual wear-and-tear. However, slipped discs, and their recurrence, can be minimised by following these simple measures:
- Practice and maintain proper posture
- Refrain from staying in one sitting or standing position for a long time
- Practice good ergonomics, especially when lifting heavy objects. Bend your knees, squat and lift with your legs.
- Exercise regularly. Low-impact sports and aerobic exercises such as swimming and walking, and stretching programs like yoga and Pilates can help improve flexibility, and strengthen and support the back.
- Stay at a healthy weight. Being overweight can put excessive pressure on the spinal discs.
- Quit smoking. Smoking can increase the risk of spinal disc injuries.
Dr Chua Soo Yong is an orthopaedic and spine surgeon recognized in Singapore for his expertise in complex spinal surgeries, which cover herniated disc treatment, nerve decompression, instrumented fusion and total disc replacement.
Atlas Orthopaedic Group is an Orthopaedic Clinic specializes in the treatment of orthopaedic ailments such as sports injuries and degenerative limb conditions. Dr Chua is accredited at all Parkway Group Hospitals, including Mount Elizabeth Orchard, Mount Elizabeth Novena, Gleneagles Hospital and Parkway East Hospital. To schedule an appointment with Dr. Chua Soo Yong, call 6262-0555 or email drchua@aog.com.sg.